29.11.2023
The more complete pdf version of the manual can be downloaded from here.
Summary
Below is described how to observe with PEPSI Permanent Fiber Unit (PFU) at Large Binocular Telescope (LBT). All pictures can be clicked to enlarge them for details.
The first part of the document describes what one should take into account when planning the observations.
Observations themselves are performed with following steps:
I Accessing PEPSI GUI
II Connecting with PFU
III Selecting and sending targets to LBT
IV Guiding
V Observing
The document also describes following items:
VI Viewing obtained spectra
VII Estimating S/N
VII Calibration frames
IX Telemetry
X Troubleshooting
Planning the observations:
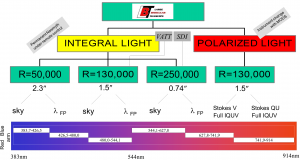
- PEPSI can be used in several observing modes:
- Wavelength coverage:
- The entire spectral range is from 383 to 912 nm but it can not be covered by a single exposure
- PEPSI has two arms, blue and red, that cover spectral ranges 383-544 nm and 544-912 nm, respectively
- Each arm has three cross-dispersers:
- CD1 383-426 nm in blue arm
- CD2 426-480 nm in blue arm
- CD3 480-544 nm in blue arm
- CD4 544-627 nm in red arm
- CD5 627-741 nm in red arm
- CD6 741-912 nm in red arm
- Simultaneously, one can observe one wavelength region in blue and one in red, however, CDs 3 and 4 can not be used at the same time
- Spectral resolution:
- Observations can be done using three different fibers (select image slicer accordingly), that is with three different resolutions:
- 100 μm gives R=250,000
- 200 μm gives R=130,000
- 300 μm gives R=50,000
- Observations can be done using three different fibers (select image slicer accordingly), that is with three different resolutions:
- Exposure times :
- Exposure time depends on the target, the wanted resolution, and used cross-disperser (use Exposure Time Calculator)
- One can have different exposure times and numbers of exposures for cross-dispersers in blue and in red arm (examples below)
- 30 min in blue, 20 min in red ⇐ red is idle for 10 minutes
- 30 min in blue, 2×15 min in red ⇐ both are ready around the same time
- 3×10 min in blue, 6×5 min in red ⇐ both are ready around the same time, blue likely idle for some minutes due to read-out times (~ 80 sec / read-out)
- Additional setups:
- The blue mirror is the default setting
- Red mirror can be used in a special case with 100 μm fibre
- If interested in good radial velocity stability, simultaneous fabry-perot-etalon (FPE) should be on
- Filter is selected automatically according the brightness of the target. However, it can be altered on fly to adapt to any changing conditions (e.g. clouds).
- PFU beam splitter is selected automatically according the brightness of the target and cross-disperser used
- If PEPSI is used on both telescopes, filters, binning, etc. need to be changed for both sides
- The blue mirror is the default setting
- Observing limits:
- The lower limit is 26 degrees
- Finding chart:
- The field of view for guiding is 28″ so finding chart is of no use
- Observing blocks:
- At the moment observing blocks can be created only by using PEPSI GUI
I Accessing PEPSI GUI
- There are 2 options for from where the observations can be done. NOTE that for Option 2 you must request VPN access to LBTO beforehand – at least 10 days before the run. Write to ScienceOps@lbto.org to get it!
- Option 1: use the PEPSI 4K monitor in the LBT control room
- Option 2: observe remotely (4K monitor helps if you want to see everything at once.)
- first make a VPN connection to vpn.lbto.org (using Cisco AnyConnect)
- then either open a VNC program and take connection to server alpha.pepsi.lbto.org:1 (or :2) or type in terminal vncviewer alpha.pepsi.lbto.org:1
- The PEPSI user interface program should be kept running all the time.
II Connecting with PFU
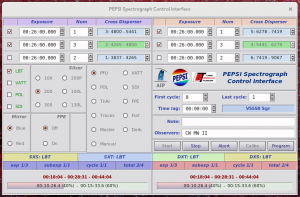
- Now you should have ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface’ open.
- In case PEPSI has been used for solar observations (SDI selected) and you have text ‘Waiting for Sun‘ in the ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface‘, click ‘Abort‘ to be able to start night observations.
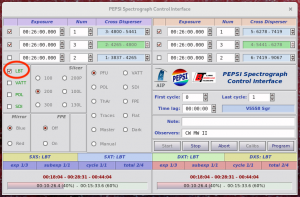
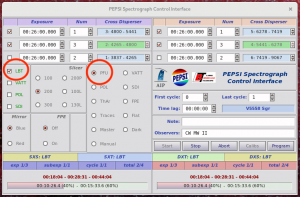
- Click on LBT check button to connect and open ‘PEPSI@LBT‘:
- Check that PFU radio button is selected:
- A ‘PEPSI@LBT‘ window should appear:
- The spectrograph has to be engaged (‘Engage‘ button) into observing mode, so that the hatches are opened for authorized sides and ADC is following the target elevation even for a pointing star.
III Selecting and sending targets to LBT
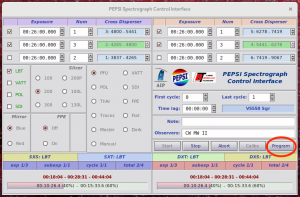
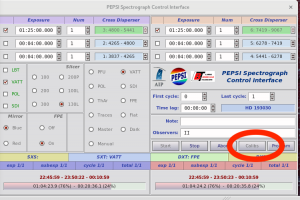
- Click ‘Program’ button on ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface’:
- When you
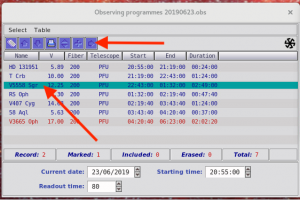
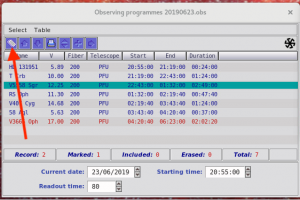
- already have an observing program, a ‘Observing Programmes‘ window and a ‘Target Visibility Plot‘ window opens. If not, go to ‘Table‘ menu, choose ‘Open or Close Table‘ and select the correct one.
-
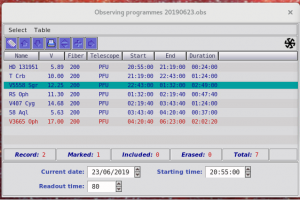
- If GUI had to be restarted, check that the correct program is open (YYYYMMDD.obs)!
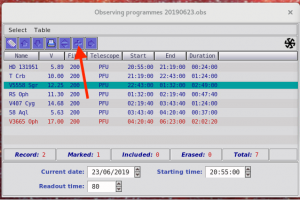
- select the target (highlighted with teal color) you want to observe and send it to LBT. This does not yet move the telescope!
- check that ‘PEPSI@LBT’ has the same target as you chose, or resend:
- check that ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface’ changed (target name, selected cross-dispersers, exposure time, etc.) according to selected target:
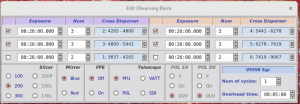
- if you need to change pre-defined exposure times, click ‘Edit fields’:
- a new window pops up and you can make the changes
- you can also change values in ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface’ directly, but then the visibility plot does not change and block will not remember the changes made in future
-
- don’t have any targets or you want to change targets
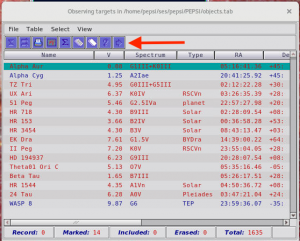
- click ‘add another object’ in ‘Observing programmes’ window:
- a new window having targets pops up:
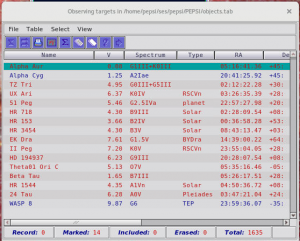
- NEVER delete targets from this list!
- Targets can be added to the catalogue:
- when one starts to write the name, it is shown if the target already is in the catalogue
- if the target already was in the catalogue and it has a PID (program ID) that is not yours, PID should be changed so that the data goes to the right person
- in case it indeed is a new target, make a query and then apply to that it goes to the catalogue
- targets can be imported from a text file
- names should be in that case in format HD123 or “HD 123”
- text file can contain also coordinates
- if the target is a transient or nova, coordinates can also be given
- for non-sidereal targets like Io or Jupiter, a name and approximate coordinates should be given and telescope uses then a special mode to observed them (talk with your telescope operator)
- when one starts to write the name, it is shown if the target already is in the catalogue
- choose the target and send it to the observing block:
- continue as in III-2-a.
- already have an observing program, a ‘Observing Programmes‘ window and a ‘Target Visibility Plot‘ window opens. If not, go to ‘Table‘ menu, choose ‘Open or Close Table‘ and select the correct one.
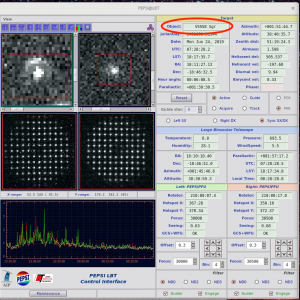
- after the telescope operator gives the permission, click ‘PRESET‘
-
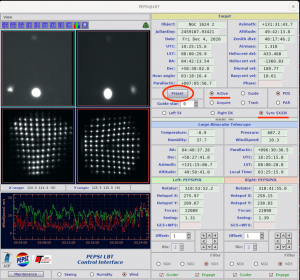
- ‘PRESET‘ to next target can be done already during CCD readout.
- Sync SX/DX mode of preset is the normal case
- In case one of the telescope eyes does not move to the target, it is possible to make ‘PRESET‘ separately only with one of them (Left SX or Right DX):
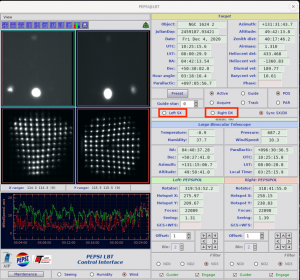
- Note that ‘Preset‘ can be done in four different modes, but only the first one should be used unless requested otherwise by the telescope operator:
- Active – the normal mode, uses wavefront sensor and guiding
- Guide – no wavefront sensor is used, guiding yes
- Acquire – only points and centres on hot spot
- Track – only points
-
IV Guiding
Collimating, guiding, and also focusing is done by the telescope operator. Do not do anything unless asked.
- ‘Engage‘ should have been checked in the very beginning but at latest at this point. It opens the hatches so that the telescope operator can put the star in the position.
V Observing
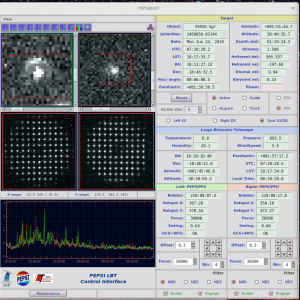
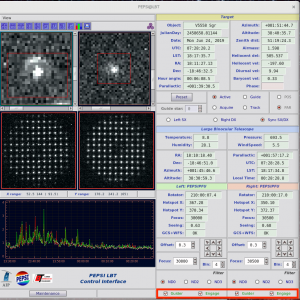
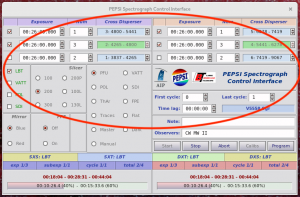
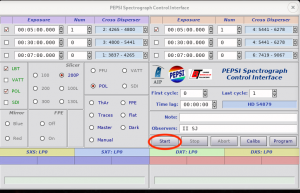
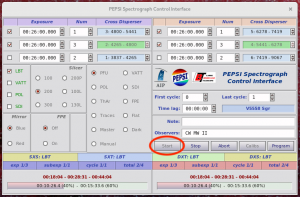
Start observations by clicking ‘Start’ in ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface’:
- This also starts guiding on both sides
- If the exposure needs to be interrupted for any reason, use ‘Stop’ in case you want to save the data obtained so far or ‘Abort’ in case the exposure time was not long enough for useful data.
- If due to the, for example, clouds you think that exposure time was not long enough, it can be changed on fly in the ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface’ as long as CCD readout has not started.
VI Viewing obtained spectra
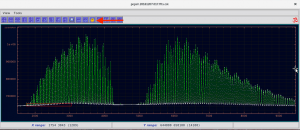
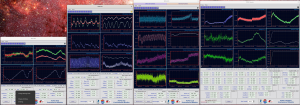
It is good to take a look at the spectra in order to see if you should change exposure times etc.
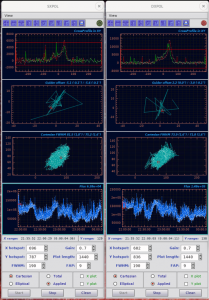
- Select the spectrum (highlighted with teal colour) you want to look at from ‘FITS Image Browser‘ with Enter or click the arrow icon to send it to ‘Spectrum viewer‘. One can also look at multiple spectra by selecting them and clicking double arrow icon.
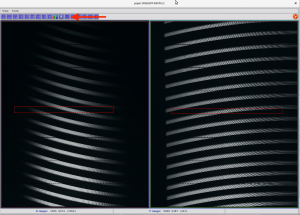
- The active window in ‘Spectrum viewer‘ has a cyan frame. Select the area you want to look at closer by drawing a red box with, for example, a mouse:
- To see a summed spectrum from selected area
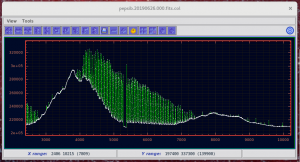
- Now you have a spectrum plot where you can see the ADUs:
VII Estimating S/N
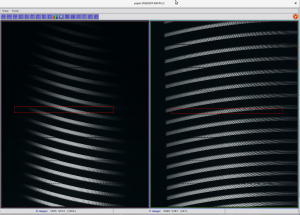
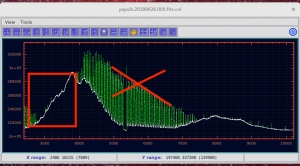
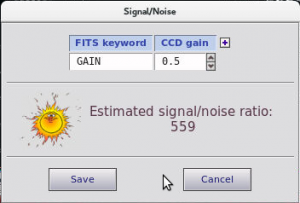
- Select an area with mouse from highest continuum values to lowest (don’t be distracted by high fabry-perot peaks):
- Click ‘Sun‘ icon on top of the spectrum viewer:
- You get a pop-up window there the S/N estimate is given, save that information into fits list by clicking ‘Save‘:
VIII Calibration frames
After the observing night is over, it is time to take the calibration
frames. Check that you have stopped guiding and guider camera is on pause.
In the ‘PEPSI Spectrograph Control Interface’ window:
- Click ‘Calibs‘ button to get a pop-up window:
- Check that for wanted fiber(s) ThAr, FPE, and Traces are chosen:
- Click ‘START‘ button on Control Interface window:
- When calibration frames are ready, click ‘Calibs‘ again to close the calibration sequencer window and to be able to do anything else.
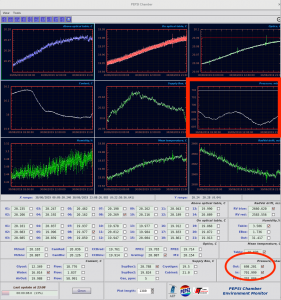
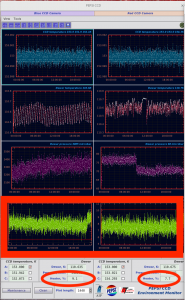
IX Telemetry
-
- It is essential to check the telemetry from time to time:
- If something is wrong and you are not trained to fix the problem, contact a person who is!
- The most important is the ‘Pressure‘ in PEPSI Chamber window. If ‘In’ value has red background, and one sees that pressure curves follow each others, everything is not fine.
- Other important measure is ‘Dewar heater‘ in PEPSI CCD window. If it approaches 0, the dewar pressure rises and pumping is needed.
X Troubleshooting
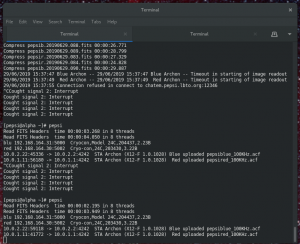
- Sometimes the software program freezes or even crashes (STA Archon time out). If that happens, find the following terminal
and type Ctrl+c and start all over again.
If terminal gives ‘Lost connection with Camera’, one can go to ‘PEPSI Control Unit’ Maintenance, but in order to do that, you should know what you are doing. Moxa-Power-Ccd Controllers, wait 10 seconds. In case of pressure problem, use again Maintenance.