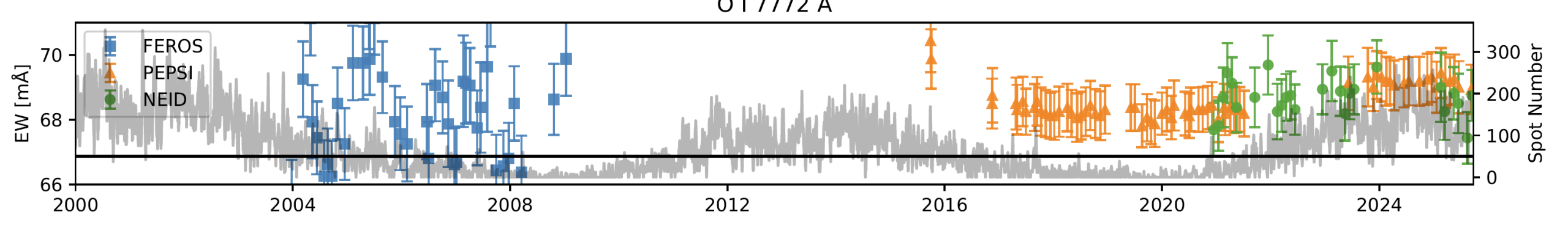
The determination of the solar oxygen abundance remains a central problem in astrophysics, as its accuracy is limited not only by models but also by systematics. While many of these factors have been thoroughly characterized, the effect of the solar activity cycle has so far remained unexplored. Due to its relative strength and accessibility, the O I infrared triplet is typically the primary choice for abundance studies. However, previous investigations have shown that abundances inferred from this triplet tend to be higher than expected on active stars, whereas such an overabundance effect is not observed for the much weaker forbidden O I 6300 Å line. This raises the question of whether a similar trend can be found for the Sun. To address this question, we analyze two decades’ worth of synoptic disk-integrated Sun-as-a-star datasets from the FEROS, HARPS-N, PEPSI, and NEID spectrographs, focusing on the infrared triplet (7772, 7774, 7775 Å) and the forbidden O I 6300 Å line. The excellent signal-to-noise ratio of the PEPSI observations allows us to detect a weak but significant variation in the equivalent widths of the infrared triplet, corresponding to about 0.01 dex difference in abundance between activity minimum and maximum. This value is significantly smaller than the typical uncertainties on the solar oxygen abundance. Due to higher scatter, no comparable trend is found in the other data sets. Based on these results, we conclude that within the typical uncertainties presented in other works, we can assume the inferred solar oxygen abundance to be stable across the solar cycle, but that this effect may be significant for other, more active stars.
Read more: Pietrow et al. 2026, A&A, in press. arXiv:2601.15919