The solar eclipse of 2017 August 21 was observed with the Potsdam Echelle Polarimetric and Spectroscopic Instrument (PEPSI) on the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT), which is located at Mt. Graham International Observatory (MGIO), Arizona, USA. At this location, a partial eclipse was observed with maximum obscuration of 61.6%. The 11-millimeter-aperture, binocular Solar Disk-Integrated (SDI) telescope, located on the kitchen balcony of the LBT building, feeds sunlight to PEPSI, which has recorded a total of 116 Sun-as-a-star spectra in the wavelength range of 5300 – 6300 Å, with a spectral resolution R=250,000 and S/N of about 733:1. The temporal evolution of the Fraunhofer Na I D doublet at 5890/5896 Å is analyzed using contrast profiles that illustrate subtle changes in the spectral line, not obvious in the intensity profiles.
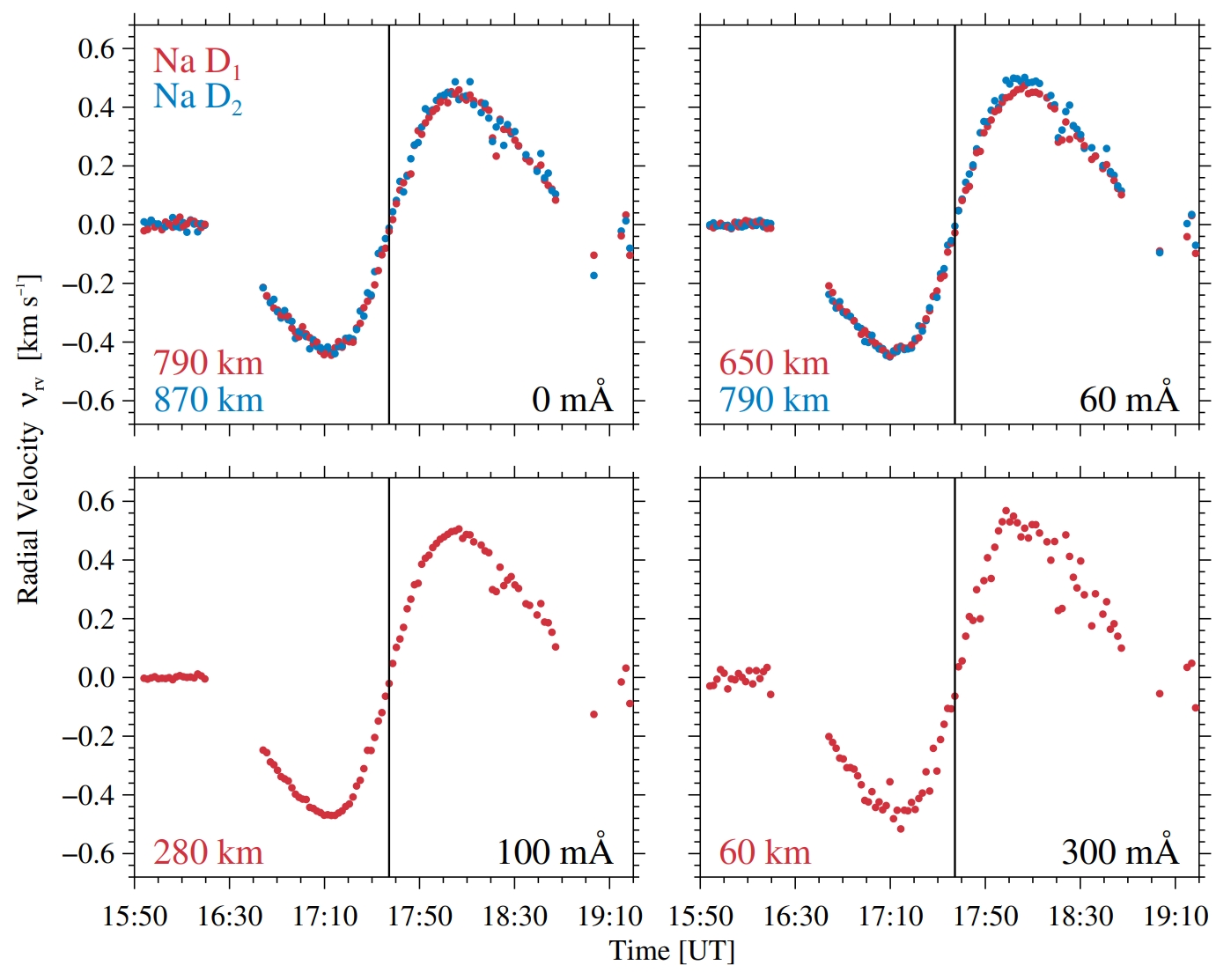
Read more: Dineva et al., 2024, Sol. Phys. 299, 123
